| Version 12 (modified by dac, 9 years ago) (diff) |
|---|
TuiView
TuiView is an open source data viewer similar to ENVI / ERDAS Imagine, the initial development was funded Landcare Research NZ Ltd. It is build on top of GDAL and is capable of opening any data formats GDAL can read, including BIL, BSQ and GeoTiff. NERC-ARF-DAN have contributed a number of features to TuiView for better handling of hyperspectral data.
Within NERC-ARF it is used as a general image viewer for hyperspectral data and DEMs and as part of the procedure for determining SCT values.
TuiView is opened from the command prompt by typing:
tuiview
Add images using the 'Add Raster' button in the top left, select the format from the dropdown menu. It is also possible to add zipped bil files (such as those NERC-ARF deliver) by selecting 'All files' and clicking on the .zip file.
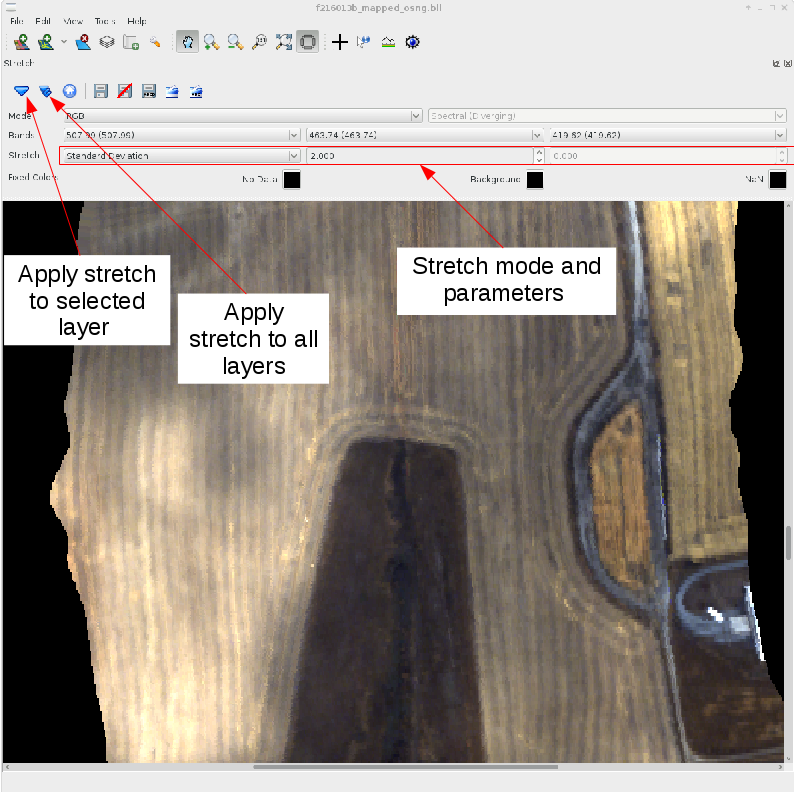
The range of pixel values within an image often does not fall between 0 - 255, as required for display, therefore it is necessary to 'stretch' the values for display. Within TuiView the stretch of the image is adjusted using the 'stretch' dialogue, brought up by through the 'edit -> stretch' menu or right clicking a layer in the list of layers. Within the stretch dialogue the bands displayed and the type of stretch can be selected. A standard deviation stretch which will scale the pixel values to from the image mean - n*standard deviation to the image mean + n*standard deviations. The stretch can be applied to a single image (single arrow) or all open images (multiple arrows) as shown below.
You can set up the default stretch to apply using the File -> Default Stretch dialogue. There are a number of rules which can be set to determine which stretch to apply given the number of bands in an image and if a colour table is present or not. Changing rule 2 (single band - no colour table) and rule 3 (three bands - no colour table) to use a standard deviation stretch, rather than the default of none is a good idea. The stretches are stored in the TuiView preferences file (~/.config/Viewer/viewer.conf), a config file with rules for NERC-ARF data is attached to this page.
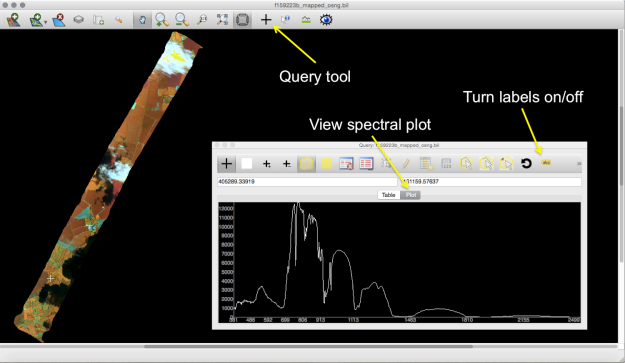
It is possible to get pixel values and view spectral profiles of the top image layer using the query tool and selecting 'plot' in the pop up as shown below. Where wavelengths are stored in the header file these will be used for the x-axis.
TuiView will not open unmapped (e.g., level1b) files by default and will give an error about only allowing north-up images. You can force TuiView to open them by setting the environmental variable TUIVIEW_ALLOW_NOGEO using:
export TUIVIEW_ALLOW_NOGEO=YES
on Linux/OS X, or:
set TUIVIEW_ALLOW_NOGEO=YES
on Windows.
If you get an error that TuiView is unable to open the file it could be that ‘data ignore value = 0′ is set in the header and the GDAL driver is unable to handle it. You can export the environmental variable:
export GDAL_PAM_ENABLED=ON
on Linux/OS X, or:
set GDAL_PAM_ENABLED=ON
on Windows. This will create a ‘*.aux.xml’ metadata file with additional features the driver doesn’t support when TuiView opens the file. More information is available in the GDALPamDataset documentation.
To speed up the display of images within TuiView you can calculate approximate statistics (used to stretch the data) before opening using:
gdalinfo -stats -approx_stats filename.bil > /dev/null
This will create an aux.xml file corresponding to the image containing the statistics which TuiView can read.
For more details on general TuiView usage see the TuiView wiki
Attachments (3)
- tuiview_spectral_profile.png (74.8 KB) - added by dac 11 years ago.
- tuiview_stretch.png (296.3 KB) - added by dac 11 years ago.
-
viewer.conf
(2.8 KB) -
added by dac 10 years ago.
TuiView config file
Download all attachments as: .zip